第12天
哪吒 2023/6/15
# 第12天
学习新知识很棒,但也要注意保护好自己的身体哦~
# Java Number & Math 类
今天认识 当需要使用数字的时候,我们通常使用内置数据类型,如:byte、int、long、double 等。
所有的包装类(Integer、Long、Byte、Double、Float、Short)都是抽象类 Number 的子类。
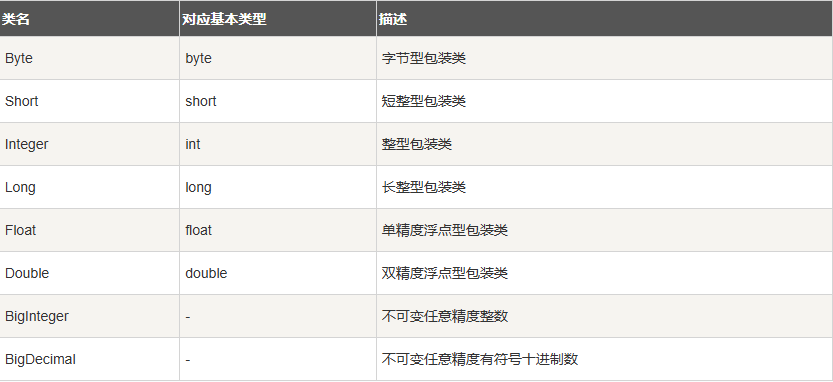
int a = 5000;
float b = 13.65f;
byte c = 0x4a;
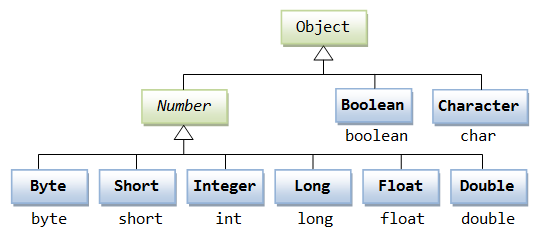
这种由编译器特别支持的包装称为装箱,所以当内置数据类型被当作对象使用的时候,编译器会把内置类型装箱为包装类。相似的,编译器也可以把一个对象拆箱为内置类型。
示例
public abstract class Number implements Serializable {
// 抽象方法
public abstract int intValue();
public abstract long longValue();
public abstract float floatValue();
public abstract double doubleValue();
// Java 8 新增
public byte byteValue() {
return (byte)intValue();
}
public short shortValue() {
return (short)intValue();
}
}
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
Integer x = 5;
x = x + 10;
System.out.println(x);
}
}
Number num = 1234.56; // 实际是Double类型
System.out.println(num.intValue()); // 1234 (截断小数)
System.out.println(num.longValue()); // 1234
System.out.println(num.floatValue()); // 1234.56
System.out.println(num.doubleValue()); // 1234.56
Integer x = 10;
Double y = 10.0;
// 正确比较方式:转换为同一类型后比较
System.out.println(x.doubleValue() == y.doubleValue()); // true
# 特殊数值处理
处理大数
BigInteger bigInt = new BigInteger("12345678901234567890");
BigDecimal bigDec = new BigDecimal("1234567890.1234567890");
// 大数运算
BigInteger sum = bigInt.add(new BigInteger("1"));
BigDecimal product = bigDec.multiply(new BigDecimal("2"));
数值格式化
NumberFormat nf = NumberFormat.getInstance();
nf.setMaximumFractionDigits(2);
System.out.println(nf.format(1234.5678)); // "1,234.57"
# 自动装箱与拆箱
// 自动装箱
Integer autoBoxed = 42; // 编译器转换为 Integer.valueOf(42)
// 自动拆箱
int autoUnboxed = autoBoxed; // 编译器转换为 autoBoxed.intValue()
# Java Math 类
public class Test {
public static void main (String []args)
{
System.out.println("90 度的正弦值:" + Math.sin(Math.PI/2));
System.out.println("0度的余弦值:" + Math.cos(0));
System.out.println("60度的正切值:" + Math.tan(Math.PI/3));
System.out.println("1的反正切值: " + Math.atan(1));
System.out.println("π/2的角度值:" + Math.toDegrees(Math.PI/2));
System.out.println(Math.PI);
}
}
高级数学运算
- 指数对数运算
Math.exp(1); // e^1 ≈ 2.718
Math.log(Math.E); // ln(e) = 1
Math.log10(100); // log10(100) = 2
// 生成[0.0, 1.0)之间的随机数
double random = Math.random();
// 生成[1, 100]的随机整数
int randomInt = (int)(Math.random() * 100) + 1;
Math.hypot(3, 4); // 计算sqrt(x²+y²) → 5.0
Math.IEEEremainder(10, 3); // IEEE余数 → 1.0
Math.PI; // π ≈ 3.141592653589793
Math.E; // 自然对数底数e ≈ 2.718281828459045
# Math 的 floor,round 和 ceil 方法实例比较
今天的内容消化得如何?下一篇会带来更多精彩内容哦~